
Diabetes can affect us in different ways. Either we are already diagnosed with it or at risk of having it, or maybe one of our loved ones has it. This certainly makes us more interested in diabetes related information and we want to be aware of some practical tips to help improve the quality and the quantity of the food we consume.
While trying to make better dietary choices and plan your meals, you might have already come across some terms such as Carbohydrates counting, Glycemic Index and Glycemic Load. You may have wondered if these are important for you to understand, and if you should keep them in mind while making strategic choices for your everyday eating.
In this regard, we have gathered some essential information that was proven to effectively help people with diabetes in finding the most adapted healthy habits to their needs.
How do Carbs affect your blood sugar?
Carbohydrates also known as Carbs are our major source of energy. They are presented in 3 main types: sugars, starches and fiber which are essential for every person with or without diabetes.
When we eat or drink foods containing carbohydrates, our body breaks down the sugars and starches into a simple sugar: the glucose, which passes to the bloodstream and is used to fuel up the body. Fiber, being a different kind of carbohydrates, is not broken down during the digestion and passes through the body relatively intact.
Now while choosing and buying your food, you can read on the Food Labels and Nutrition Facts of some of the foods, the term “Total Carbohydrates” which refers to all 3 types of Carbs.
Eating all forms of Carbs when having diabetes is possible, but we need to understand how these Carbs affect our blood sugar levels and how to simply find our balance by making better food choices. This will help to keep blood sugar under control and prevent other complications and health issues.
Our goal is to learn how to choose our carbohydrates foods; we want to go for foods with healthful, nutritious carbs, they are rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals and low in sugars, sodium, and unhealthy fats.
In fact, the carbohydrates foods that we consume have different nutritional properties that determine how quickly and easily our body processes them, and how blood glucose is then affected.
Now as we are trying to keep diabetes under control, we want to understand how the foods we choose affect our blood sugar; we still want to eat the foods that we enjoy to eat but we just need to adjust our meal plans and our cooking style so we can keep that blood sugar on target!
Glycemic Index and its importance for managing Diabetes
An important concept you certainly want to become familiar with is the Glycemic Index also shortly known as GI.
This Index will help you to understand the impact of the quality of the food you choose on your after-meal blood sugar level. You will also learn how to easily make lower glycemic index food choices (low GI foods) for your everyday healthy meals.
So what is a Glycemic Index and what I need to know about it?
- The Glycemic Index of a food is a number ranging from 0 to 100 that is assigned to different tested foods; it represents the relative rise in blood glucose level two hours after consuming that food.
Each value of a GI of a food is based on much that food item raises your blood glucose level compared with how much pure glucose raises your blood sugar level.
The number 100 is arbitrarily given to glucose. - The Glycemic Index is representative of the quality of the carbohydrate that you are eating in your food. It also gives an idea of how a specific carbohydrate is digested and absorbed by the body compared to the glucose.
- Scientific research methods have allowed for assigning GI values to many carbohydrate foods that we consume. This has allowed to divide the tested foods into low GI foods, medium GI foods and high GI foods according to their Glycemic Index values.
- Understanding the differences between the three categories of GI values is a great information to guide us in making healthier food choices and easily manage diabetes.

Low GI-from 1 to 55 Foods with low GI index are healthier choices and should be included more often in everyday diet.
Medium GI- from 56 to 69 Foods with medium GI index should be consumed with more caution.
High GI- 70 and higher These foods should be consumed with extra caution when a person has diabetes. This does not mean that you cannot try them, but it is not recommended to have them on a regular basis and with uncontrolled amounts.
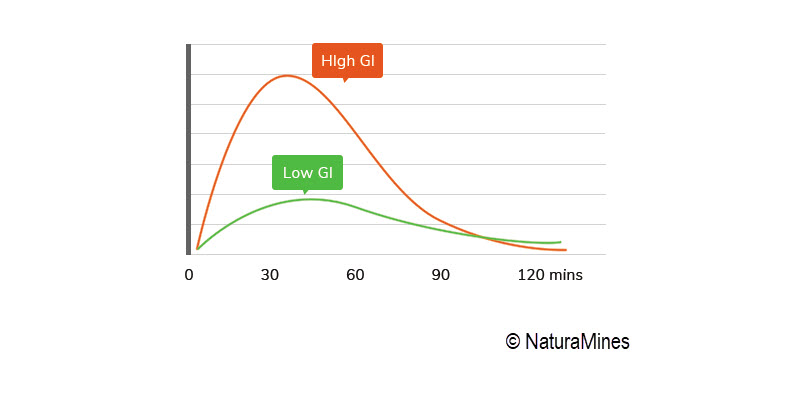
Comparison of blood Glucose level 2 hours after consuming a high GI food and a low GI food
If we compare the level of blood sugar in the body 2 hours after consuming a high glycemic index food with the level of blood sugar after eating a low glycemic index food, we can easily notice how the body responds very differently to the two different types of food.
While eating a high GI food causes a quicker blood glucose rise, also known as sugar spike; the consumption of a lower GI food shows lower blood glucose levels that is maintained for a longer period of time.
Do you want to know more about diabetes and how to keep it under control ?










Discussions
Add Comment